- 1 Outline of the Article
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 What is Artificial Intelligence?
- 1.3 The Evolution of AI So Far
- 1.4 Current Trends in AI
- 1.5 AI in Business and Industry
- 1.6 AI in Healthcare
- 1.7 The Role of AI in Education
- 1.8 AI and the Future of Work
- 1.9 The Rise of AI Ethics
- 1.10 AI and Data Privacy
- 1.11 The Impact of AI on Society
- 1.12 AI in Entertainment and Media
- 1.13 AI and Autonomous Systems
- 1.14 The Future of AI: Predictions
- 1.15 Conclusion
- 1.16 FAQs
Outline of the Article
- Introduction
- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- The Evolution of AI So Far
- Current Trends in AI
- AI in Business and Industry
- AI in Healthcare
- The Role of AI in Education
- AI and the Future of Work
- The Rise of AI Ethics
- AI and Data Privacy
- The Impact of AI on Society
- AI in Entertainment and Media
- AI and Autonomous Systems
- The Future of AI: Predictions
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a concept of science fiction to a reality that influences many aspects of our lives. From voice-activated assistants like Siri and Alexa to personalized recommendations on Netflix, AI is already here, and it’s changing the way we interact with technology. But what does the future hold for AI? As we look ahead, it’s crucial to understand where AI is heading, its potential benefits, and the challenges that come with it.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules for using it), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction.
- Narrow AI: Also known as weak AI, this type is designed to perform a narrow task (e.g., facial recognition or internet searches). It operates under a limited set of constraints and parameters.
- General AI: This form of AI can theoretically perform any intellectual task that a human can do. It’s capable of learning, understanding, and reasoning on a level comparable to humans.
- Superintelligent AI: A speculative form of AI that surpasses human intelligence across every field, from scientific research to social skills.
The Evolution of AI So Far
The journey of AI began in the mid-20th century, with the concept of machines that could think introduced by mathematician Alan Turing. Over the decades, AI has seen significant developments:
- 1950s-1960s: The inception of AI research and the development of early algorithms.
- 1970s-1980s: The introduction of expert systems that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert.
- 1990s: AI milestones like IBM’s Deep Blue defeating chess champion Garry Kasparov.
- 2000s-Present: The rise of machine learning and deep learning, led to advancements in areas such as speech recognition and autonomous vehicles.
Current Trends in AI
AI continues to grow, with several trends dominating the current landscape:
- Machine Learning and Deep Learning: These subsets of AI are crucial for pattern recognition and predictive analytics. Deep learning, in particular, has revolutionized how machines understand and interpret complex data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables machines to understand and respond to human language, which is crucial for developing chatbots, voice assistants, and other language-based applications.
- AI in Everyday Applications: AI is now part of our daily lives, from spam filters in our emails to algorithms that personalize our social media feeds.
AI in Business and Industry
AI is transforming businesses and industries by enhancing efficiency and decision-making processes.
- Automation and Efficiency: AI-powered automation is streamlining operations, reducing errors, and cutting costs. For instance, AI in manufacturing can predict equipment failures, and optimize maintenance schedules.
- AI-Driven Decision-Making: AI provides data-driven insights that help businesses make informed decisions. For example, AI can analyze consumer behavior and predict trends, allowing companies to adapt their strategies.
- Case Studies: Companies like Amazon use AI for inventory management, while financial institutions use AI to detect fraudulent activities.
AI in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is one of the biggest beneficiaries of AI advancements.
- AI for Diagnostics and Treatment: AI can analyze medical images and data to diagnose diseases like cancer with high accuracy. It can also suggest treatment options based on patient data.
- Personalized Medicine: AI enables personalized treatment plans by analyzing an individual’s genetic information, lifestyle, and environment.
- AI in Managing Healthcare Data: AI helps in organizing and analyzing vast amounts of healthcare data, leading to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare systems.
The Role of AI in Education
AI is making its mark in education by enhancing learning experiences and administrative efficiency.
- AI as a Learning Tool: AI-powered tools provide interactive learning experiences, adapting to the pace and style of each student.
- Personalized Learning Experiences: AI can customize educational content to meet the needs of individual students, improving engagement and retention.
- AI in Administrative Tasks: AI can automate administrative tasks like grading and scheduling, freeing up educators to focus more on teaching.
AI and the Future of Work
The integration of AI into various sectors is changing the landscape of work.
- Impact on Job Markets: While AI might replace some jobs, it also creates new opportunities, especially in tech-related fields.
- New Career Opportunities: As AI grows, so does the demand for AI specialists, data scientists, and other tech professionals.
- Preparing for an AI-Driven Workplace: Workers must adapt by acquiring new skills and embracing lifelong learning to stay relevant.
The Rise of AI Ethics
As AI becomes more integrated into society, ethical considerations become paramount.
- Importance of Ethical Considerations: AI must be developed responsibly to avoid misuse and ensure it benefits society as a whole.
- Potential Risks of AI: AI can be misused for malicious purposes, such as surveillance or creating deepfakes. There is also the risk of job displacement.
- Addressing Biases in AI Systems: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to unfair outcomes. Addressing these biases is crucial for fair and equitable AI solutions.
AI and Data Privacy
With AI’s capability to collect and analyze data, privacy concerns are more relevant than ever.
- AI’s Role in Data Collection: AI systems can gather vast amounts of data from various sources, including personal information.
- Concerns About Data Security: The more data AI systems collect, the greater the risk of breaches and misuse.
- Regulations and Policies: Governments and organizations must implement policies to protect data and ensure ethical AI use.
The Impact of AI on Society
AI’s influence extends beyond technology, affecting social structures and daily life.
- Social Implications of AI: AI can improve quality of life but raises concerns about privacy, security, and job displacement.
- AI in Smart Cities: AI manages traffic, energy, and waste in smart cities, making urban life more sustainable.
- Changes in Daily Life: From smart home devices to personalized shopping experiences, AI is changing our lives.
AI in Entertainment and Media

AI is revolutionizing the entertainment industry, offering new ways to create and consume content.
- AI for Content Creation: AI can generate articles, music, and even films, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
- Personalization of Media Experiences: AI algorithms provide tailored content recommendations, enhancing user experience.
- Future of AI-Generated Art and Music: AI is already creating art and music, raising questions about the role of human creativity in the future.
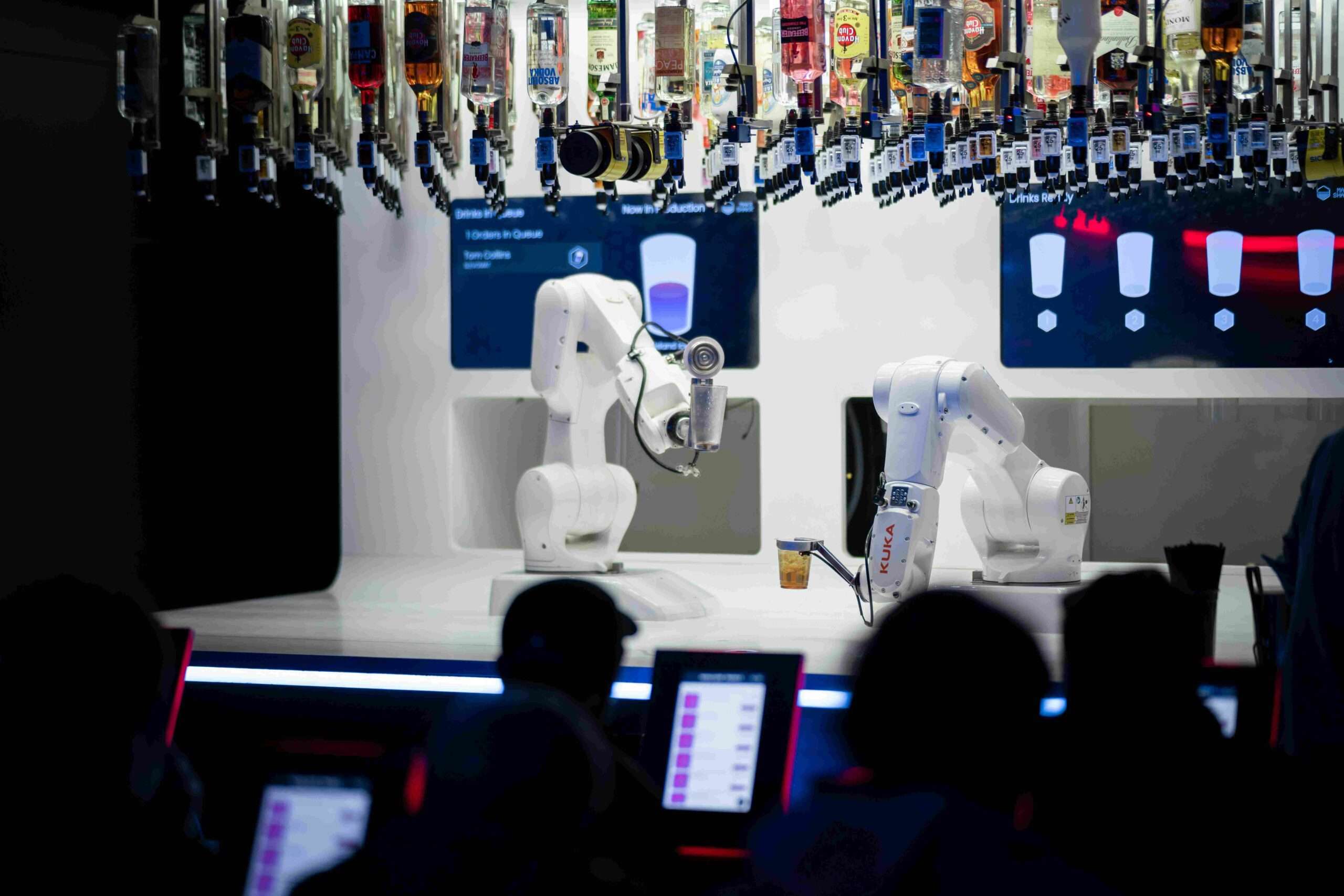
AI and Autonomous Systems
Autonomous systems, powered by AI, are becoming increasingly common.
- Self-Driving Cars: AI enables cars to drive themselves, promising safer and more efficient transportation.
- AI in Robotics: AI is used in robots for manufacturing, healthcare, and even companionship.
- Challenges of Autonomous Technology: Safety, ethics, and legal issues must be addressed as autonomous technology evolves.
The Future of AI: Predictions
What can we expect from AI in the future?
- Short-Term Advancements: Shortly, we can expect improvements in AI’s ability to understand and interact with humans and more integration into everyday devices.
- Long-Term Possibilities: In the long term, AI could achieve general intelligence, leading to significant societal changes.
- AI in Space Exploration: AI could play a crucial role in exploring and understanding space, from autonomous spacecraft to analyzing data from distant planets.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a distant dream; it’s a reality reshaping our world. From healthcare to education, AI is making life easier, more efficient, and more personalized. However, as we embrace this technology, we must also consider the ethical implications and prepare for the changes it brings. The future of AI is bright, but it requires careful thought and responsible development to ensure it benefits everyone.
FAQs
- What is the difference between Narrow AI and General AI?
- Narrow AI is designed for specific tasks, like voice recognition, while General AI can perform any intellectual task a human can do.
- How is AI used in healthcare?
- AI is used for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and managing healthcare data, leading to better patient outcomes.
- What are the ethical concerns associated with AI?
- Ethical concerns include job displacement, privacy issues, and the potential for AI to be used for harmful purposes.
- Can AI replace human creativity?
- While AI can generate art and music, human creativity involves emotion and intuition, which AI cannot replicate.
- What is the future of AI in space exploration?
- AI could help with autonomous spacecraft, analyzing data from distant planets, and making space exploration more efficient.

One thought on “The 14 Future of Artificial Intelligence AI: What to Expect”