The manufacturing industry is rapidly evolving due to the increasing integration of robotics. While some manufacturing units follow complete manual processes, industries with fully automated processes exist. However, the innovation in the robotics industry has introduced something in between these two. Collaborative robots bridge the gap between complete manual and automated manufacturing processes. Popularly known as cobots, these robots are a significant asset in the production industry due to their versatility and scalability.
If you want to understand what cobots are and how they shape the manufacturing industry, continue reading below. This post will delve into the specifics of manufacturing collaborative robots and differentiate between cobots and traditional robots.
What are Collaborative Robots?
Collaborative Robots, nicknamed Cobots, are a more approachable alternative to traditional robots. They are designed to work collaboratively with human employees. These are safe to work with and do not require safety barriers if appropriate risk assessments are conducted. Cobots are built for safety and flexibility. This allows them to perform various tasks of varying complexity. Also, these work intuitively, making it easier for non-robotic experts to handle and program them.
Earlier, cobots were not accessible enough. They came from industrial robots that were large and expensive. Also, traditional industrial robots were confined to safety cages as they were not safe for human collaboration. However, the invention of modern collaborative robots in manufacturing is a more approachable alternative to traditional robots. They are safe for human interaction and collaboration.
Cobots are also much less expensive and smaller in size. They are sensitive and quickly detect and respond to their environment and the humans interacting. Cobots are in high demand for flexibility and safety to enhance automation and collaboration in manufacturing units. They are agile and suitable for quick repurposing.
Cobot vs Robot
Now, let’s delve into the critical difference between cobots and robots.
- Collaboration with Humans- A cobot can ideally collaborate with humans and act as your assistant operator. These are typically used to work alongside human operators. On the other hand, traditional robots are designed and programmed to work with negligible or no human interaction. They work on completely automated tasks. Also, they usually remain in safety cages as they are unsafe for interaction.
- Safety- Cobots are designed to offer seamless collaboration. They have detection features that allow them to operate in the same environment where humans work. These robots are designed with detection features. They can be immobilised with the slightest touch, preventing injury to humans. In contrast, the traditional robots are not safe for human interaction. Safety is not their primary function; they simply focus on completing their tasks. As a result, these robots do not work in the same environment as humans and are isolated in safety fencing and cages.
- Ease of Use- Collaborative robots are designed and programmed for ease of use. They can be programmed easily, and their operation is quickly understandable. They do not require advanced coding, allowing non-experts to operate them and give work instructions without coding. Their ease of use enables human operators without coding and programming expertise to reprogram them for various tasks. Contrary to cobots, traditional robots require advanced programming and cannot be reprogrammed by non-experts.
- Functionality- Cobots can be easily shifted from one place to another to be used in different manufacturing unit areas. They are easy to mount on any surface, and their lightweight nature facilitates mobility. This is not the case with traditional robots, as they are pretty heavy.
Important Components of Cobots
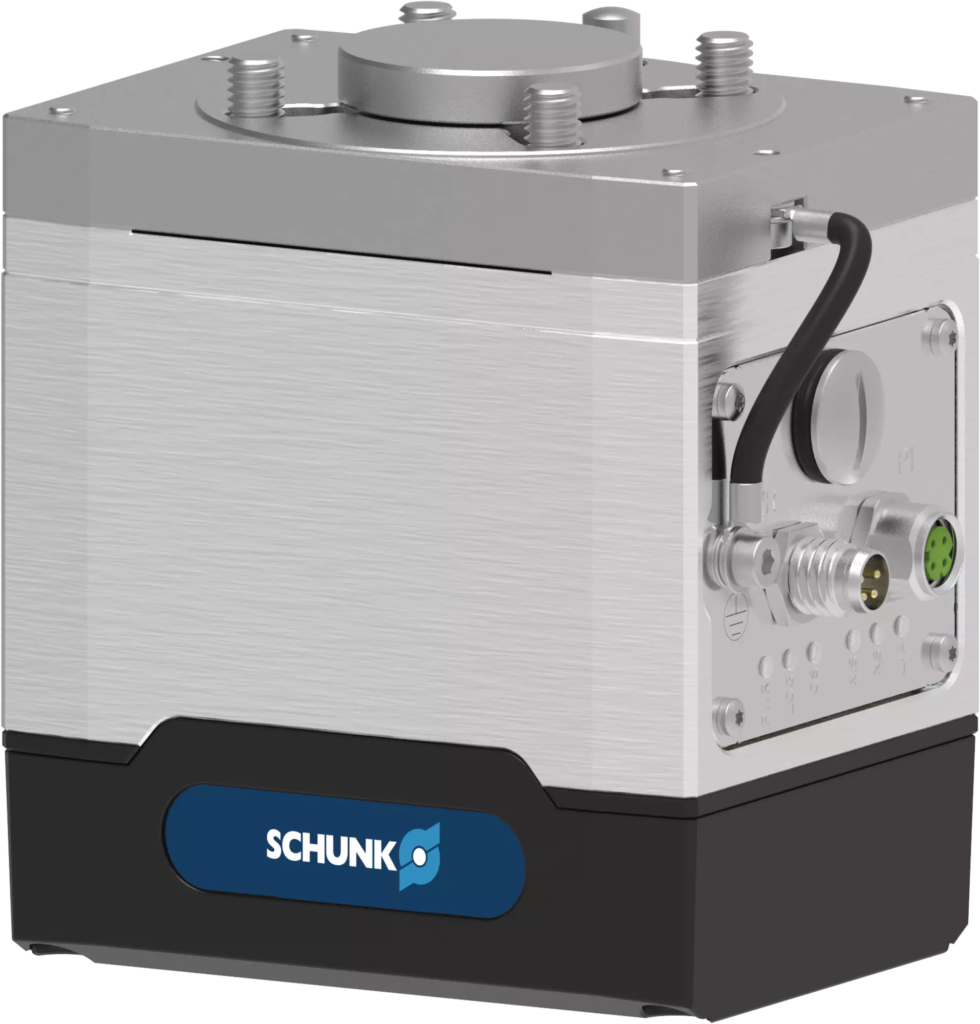

Some of the most critical components of cobots are as follows.
Collaborative Robot Arm and Joint
The collaborative robot arm is its most crucial component. It is also the most noticeable component that signifies the capability and reach of the robot. Cobots might have single-arm or multiple-arm configurations. The single-arm cobots have a streamlined structure that allows them to work in confined spaces. On the other hand, multiple-arm cobots are designed to perform complex tastes that use both hands to mimic human coordination.
A collaborative robot arm is brought to life by its joints. These are the critical points of articulation, also known as the axis. The joints allow the cobot’s arms to bend, rotate and extend. These points provide them with a range of motions that are precise and versatile. Usually, one arm has 4 to 10 joints, exceeding the capabilities of a human hand. Joints are of two types- linear and rotatory.
End-Effectors
End-effectors are also significant components of cobots. These tools empower these robots to interact with other tools and objects. An end-effector is a point of contact between the product or workpiece and the cobot. They must be compatible with the weight and interface of a cobot’s arm. End-effectors used in a cobot are not randomly chosen. They depend on the material’s nature handled by a cobot, like the material’s fragility, weight and size. Some of the most significant end effectors include-
- Grippers
- Tool Changers
- End-of-Arm Tooling
- Vision Systems
- Range Extenders
- Feeding Systems
Sensors and Safety Components
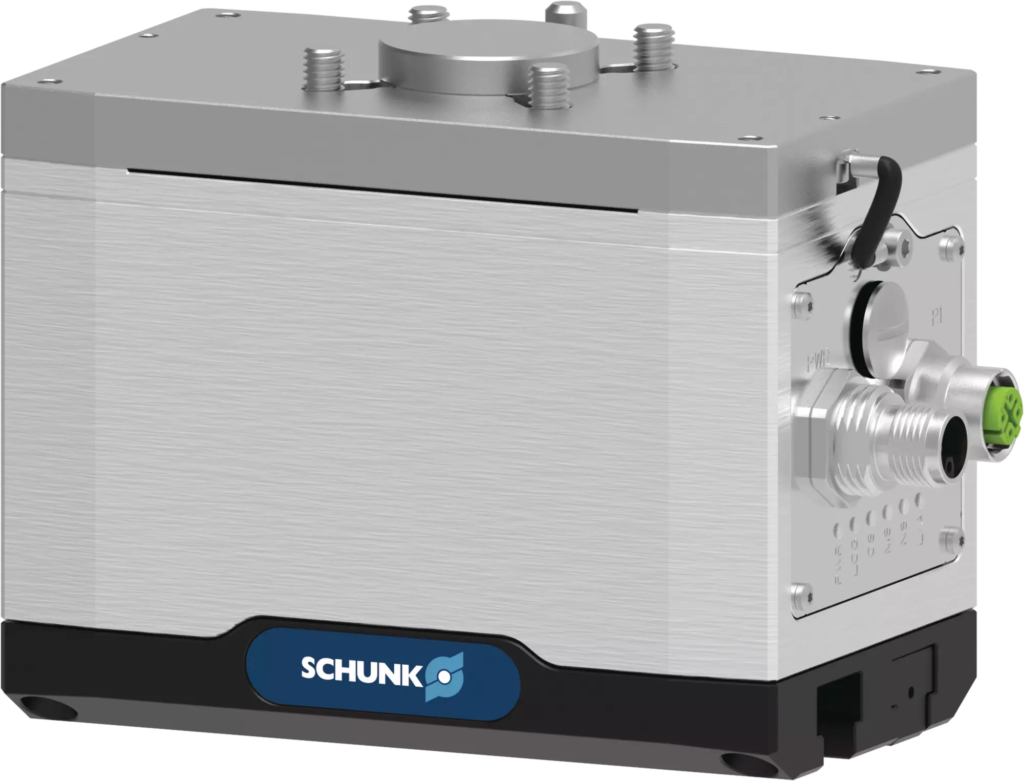

Cobots also have sensors and safety components that make them safe for human collaboration. Some of the most critical sensors and safety components in cobots are-
- Collision Avoidance Sens ors
- Force and Torque Sensors
- Pressure- Sensitive and Responsive Skins
- Proximity Sensors
- Vision Systems
- Emergency Stop Buttons
Summing Up
Various cobots, like a collaborative welding robot, are revolutionising the manufacturing industry. These innovative and approachable robots allow human operators in the manufacturing units to handle them easily without needing expertise in robotics programming.
Schunk offers the best components for cobots to make them safer and more accessible for human collaboration. We present premium quality components like collision avoidance sensors, end effectors, and others.
